Sustainable Groundwater Development • RWSN Topic

Handpump Technologies
Manual pumps have been used for centuries but this simple technology remains the mainstay of rural water supplies in many countries.
RWSN has maintained international standards for the public domain handpumps since 1992 and provided extensive technical support to many national governments, NGOs and the private sector to enable decisions to be made regarding handpump standardisation, raise manufacturing standards and build skills and systems to improve handpump operation and maintenance.
If you have a limited internet connection, then we have a flash drive with all the handpump specifications and manuals - contact the RWSN Secretariat on
The RWSN website hosts the standards, manufacturing and quality control guidelines, installation and maintenance manuals, as well as numerous studies for a wide range of handpumps in the overview below.
Are you new to the subject of handpumps?
If you want to learn about handpump technology, the handpumps most commonly used today, and how they came to dominate the market, and are interested in the current handpump challenges, we suggest that you start by reading the following documents:
|
Pump Technology and History |
Handpump challenges of today |
|
Other practical documents that you may not know about
RWSN has published maintenance manuals, and short maintenance cards for the following pumps:
- Afridev Handpump Maintenance Card (English, French & Portuguese)
- Installation and Maintenance Manual for the Afridev Handpump
- Installation and Maintenance Manual India Mark II Handpump
- India Mark II Major Maintenance Guide
- Installation and Maintenance Manual for Rope Pumps
- Maintenance Card for Rope Pump
And if you have not played top trumps (a card game that we used for training) on handpumps, try this – The Handpump Card Game!
Hand Pump Overview: see below
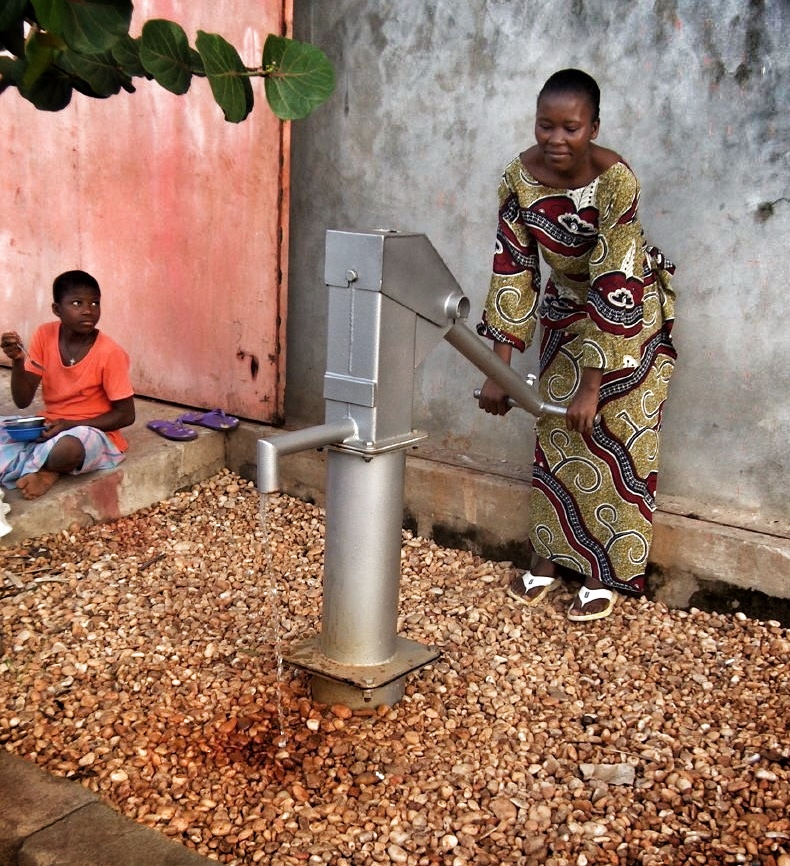 The Afridev Pump is a conventional lever action handpump. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of up to 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 45 m. The Afridev Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Afridev Pump is fully corrosion resistant, easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Afridev Pump is a conventional lever action handpump. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of up to 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 45 m. The Afridev Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Afridev Pump is fully corrosion resistant, easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
 The Afridev Pump with a Bottom Support System (BSS) is a technology that uses a reinforced version of the Afridev Pump together with a Support from the end of the borehole (BSS). It is designed for water lifting in low water table areas and the maximal lift recommended is 80 m. The Afridev Pump with BSS is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Afridev Pump with BSS is fully corrosion resistant, relatively easy to install by pump mechanics and can be maintained by the communities.
The Afridev Pump with a Bottom Support System (BSS) is a technology that uses a reinforced version of the Afridev Pump together with a Support from the end of the borehole (BSS). It is designed for water lifting in low water table areas and the maximal lift recommended is 80 m. The Afridev Pump with BSS is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Afridev Pump with BSS is fully corrosion resistant, relatively easy to install by pump mechanics and can be maintained by the communities.
 The BluePump is a lever-action reciprocating handpump that is intended to be a more rugged alternative or replacement for an Afridev or India Mark II/III. It can reportedly pump from a deep as 100m. Around 500 BluePumps are currently in operation.
The BluePump is a lever-action reciprocating handpump that is intended to be a more rugged alternative or replacement for an Afridev or India Mark II/III. It can reportedly pump from a deep as 100m. Around 500 BluePumps are currently in operation.
The BluePump was developed by Fairwater Foundation (Netherlands) and is manufactured by Boode B.V. (Netherlands) and is available in Cameroon, Burkina Faso, Central African Republic, Gambia, South Africa, Namibia and Tanzania.
 The Bush Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump, developed and standardised in Zimbabwe (SAZ 881:2004). It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. Three different cylinders are available, the smallest one extend the range to a maximum recommended lift of 80 m. The Bush Pump is not corrosion resistant. It requires special skills for installation as well as for the maintenance; it is not a VLOM pump.
The Bush Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump, developed and standardised in Zimbabwe (SAZ 881:2004). It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. Three different cylinders are available, the smallest one extend the range to a maximum recommended lift of 80 m. The Bush Pump is not corrosion resistant. It requires special skills for installation as well as for the maintenance; it is not a VLOM pump.
Peter Morgan has produced a set of Inspection training videos.
 A pump for drinking water and limited use for irrigating gardens.
A pump for drinking water and limited use for irrigating gardens.
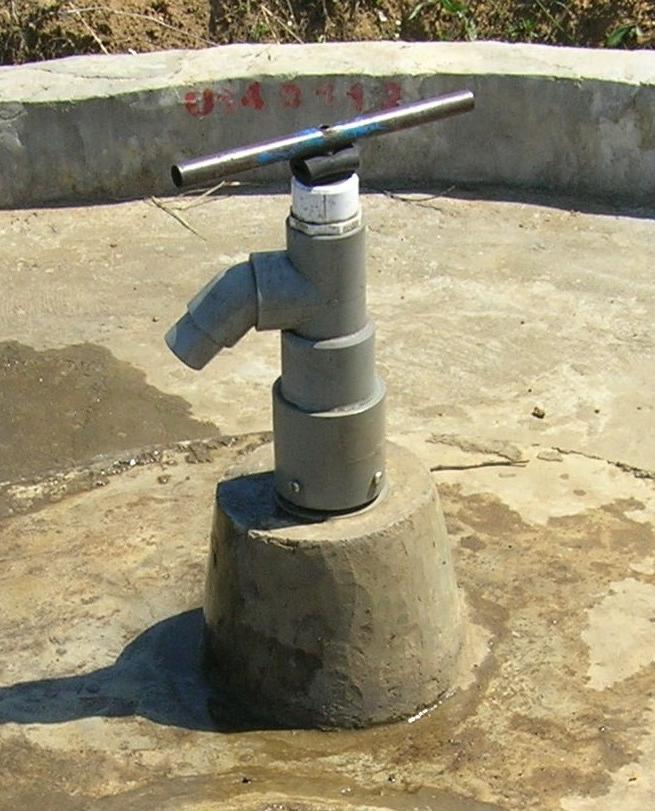
The Canzee pump is a direct action pump initially developed in New Zealand. It uses a simple pumping principle. It consists of two pipes, one slightly larger than the other. At the bottom of each pipe is a non-return valve. The pumping movement raises and lowers the inner pipe. The outer pipe remains still. When the inner pipe is raised it lifts the water contained within it. The atmospheric pres-sure pushes more water into the outer pipe. Each stroke lifts the water in the inner pipe to the top until it runs out through the spout. The pump is self-priming. A thin film of water between the two pipes ensures they do not touch: the pump lubricates itself. The Canzee pump is designed as family pump for serving user groups of about 100 to 150 people. It can be used for irrigation of family gardens. Like all direct action pump the operation is not ergonomically favourable, therefore prolonged pumping is not possible.
 A pump for drinking water and limited use for irrigating gardens.
A pump for drinking water and limited use for irrigating gardens.
The EMAS Flexi-pump is a direct action pump initially developed in Bolivia. It uses a simple pumping principle. It consists of two PE-pipes (diameter approx. 5 cm) put into one another, one slightly larger than the other. At the bottom of each pipe is a non-return valve (glass ball). A metal pipe with a T-fitting serves as handle of the pump. One side of the T has a blind nipple and the other has a discharge nipple with elbow downward. A hose can be attached to this outlet so that water can be transported away from the pump up to 300m. The pumping movement raises and lowers the inner pipe. The outer pipe remains still. When the inner pipe is raised it lifts the water contained within it. Each stroke lifts the water in the inner pipe to the top until it runs out through the T-handle. The pump is self-priming. The EMAS Flexi pump is less resistant to very intensive use and mistreatment than metal pumps. It is designed as family pump for serving user groups of about 20 to 50 people. It can be used for irrigation of family gardens. Like all direct action pump the operation is not ergonomically favourable, therefore prolonged pumping is not possible.
 The India Mark II Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 50 m.
The India Mark II Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 50 m.
The India Mark II is a public domain pump defined by Indian Standards and RWSN specifications. The India Mark II pump is not corrosion resistant.
It requires special skills for installation as well as for the maintenance; it is not considered to be a VLOM pump.
 The India Mark II Extra Deep well Pump is designed for lifting water from extra deep water sources and is therefore strongly built. The maximal lift recommended is 80 m.
The India Mark II Extra Deep well Pump is designed for lifting water from extra deep water sources and is therefore strongly built. The maximal lift recommended is 80 m.
The India Mark II Extra Deep well is a public domain pump defined by Indian Standards or RWSN specifications.
This pump is not considered to be a VLOM pump.
 The India Mark III Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump for shallow to medium deep wells. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 30 m. Besides the “Standard 63.5 mm” configuration, there exists a version with Ø50 mm cylinder size for lifts up to 50 m.
The India Mark III Pump is a robust conventional lever action handpump for shallow to medium deep wells. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 30 m. Besides the “Standard 63.5 mm” configuration, there exists a version with Ø50 mm cylinder size for lifts up to 50 m.
The India Mark III Pump is a public domain pump defined by Indian Standards and RWSN specifications. This pump requires special skills for installation and has good potential for community based maintenance.
 The Indus, Kabul and Pamir Pumps are conventional lever action handpumps. They are designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 15 m for the Kabul Pump, 45 m for the Indus Pump and 60 m for the Pamir Pump. The pumps are not fully corrosion resistant; rods are subject to rusting. The Indus, Kabul and Pamir Pumps are public domain pumps defined by RWSN specifications, only used in Afghanistan and Pakistan. They are easy to install and have excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Indus, Kabul and Pamir Pumps are conventional lever action handpumps. They are designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 15 m for the Kabul Pump, 45 m for the Indus Pump and 60 m for the Pamir Pump. The pumps are not fully corrosion resistant; rods are subject to rusting. The Indus, Kabul and Pamir Pumps are public domain pumps defined by RWSN specifications, only used in Afghanistan and Pakistan. They are easy to install and have excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Indus, Kabul and Pamir Pumps are conventional lever action handpumps. The configuration includes an “open top” cylinder: the piston can be removed from the cylinder without dismantling the rising main. The foot valve is retractable with a fishing tool.
 The Jibon Pump is a lever operated deep-set pump for shallow wells. Typically, Jibon Pumps are installed in collapsible tube wells with the screen extending to the coarse sand aquifer. It is designed for family use, serving up to 100 persons. The Jibon Pump is reasonably corrosion resistant and the maximum recommended lift is 18 m. The Jibon Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Jibon Pump is a lever operated deep-set pump for shallow wells. Typically, Jibon Pumps are installed in collapsible tube wells with the screen extending to the coarse sand aquifer. It is designed for family use, serving up to 100 persons. The Jibon Pump is reasonably corrosion resistant and the maximum recommended lift is 18 m. The Jibon Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
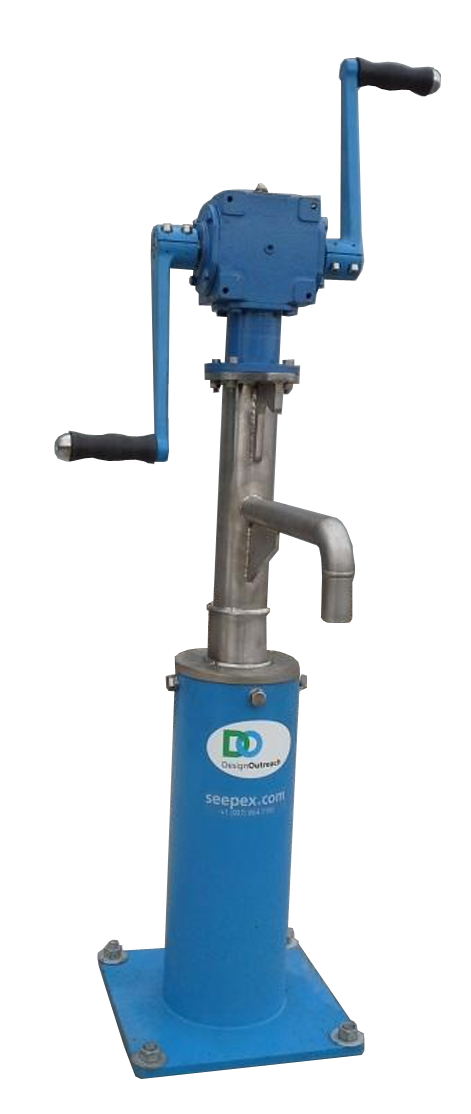 The LIFEPUMP is a new design of handpump that is currently in development and testing by a partnership of organisations being led by Design Outreach (US). It is a progressive cavity pumped based on the now-defunct Moyno design. The need was identified by Water for Good in the Central African Republic who needed a robust deepwell handpump that could reach 100-150m below ground level.
The LIFEPUMP is a new design of handpump that is currently in development and testing by a partnership of organisations being led by Design Outreach (US). It is a progressive cavity pumped based on the now-defunct Moyno design. The need was identified by Water for Good in the Central African Republic who needed a robust deepwell handpump that could reach 100-150m below ground level.
More Information
- Design Outreach
- RWSN Forum 2016 Paper: Piloting of an Innovative Deep-Reaching and Reliable Hand Pump in Africa for Rural Water Access: The LifePump [128]
- Presentation (ENGLISH)
- Chisenga, Bixler, Sitolo, Nyirenda, Muheka, Peacock (2021) Policy influence for ultra-deep reaching hand pumps. Case study for LifePump acceptance in Zambia and Malawi , RWSN , Skat Foundation , St. Gallen, Switzerland
DISCLAIMER: This is a non-RWSN handpump design and endorsement by RWSN, Skat or any of its member organisations should not be inferred.
 The Malda Pump is a direct action pump for Low Lift Wells. It uses a buoyant pump rod that helps to reduce the forces on the handle. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 15 m. The Malda Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Malda Pump is fully corrosion resistant. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Malda Pump is a direct action pump for Low Lift Wells. It uses a buoyant pump rod that helps to reduce the forces on the handle. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 15 m. The Malda Pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. The Malda Pump is fully corrosion resistant. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance.
The Malda Pump as a direct action pump is based on a buoyant pump rod that is directly articulated by the user, discharging water during the up- & down stroke.
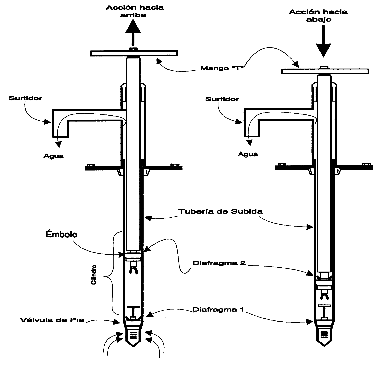 The Maya-Yaku direct action pump is a version of the Tara pump that is used in Central-America and Bolivia. It is slightly different from Tara regarding the use of materials in certain components, but the changes do not alter the basic principles of the original design.
The Maya-Yaku direct action pump is a version of the Tara pump that is used in Central-America and Bolivia. It is slightly different from Tara regarding the use of materials in certain components, but the changes do not alter the basic principles of the original design.
The simplicity of the design means that it is straightforward to maintain and repair.
 A pump for small scale irrigation and limited use for drinking water.
A pump for small scale irrigation and limited use for drinking water.
The Money Maker pump is a further development of the treadle pump also intended as a foot operated pump for small scale irrigation. The Pump sucks the water to the cylinder, then pressurizes it, sending it through a crude sprinkler over the crop. It is easy to repair and maintain The stepping movement of the operator is ergonomically favourable and makes it easy to pump for prolonged periods, thus well suited for irrigation. Typically, Money Makers Treadle placed near a river or pond and a suction hose reaches into the source. The pump installation is not fixed and the pump can be moved around. The pump is not intended for drinking water use as it takes the unprotected water from ponds or rivers.
The Nira AF-85 Pump is a direct action pump for Low Lift Wells. It uses a buoyant pump rod that helps to reduce the forces on the handle. It is designed for heavy-duty use, serving communities of 300 persons. The maximum recommended lift is 15 m. The Nira AF-85 is fully corrosion resistant. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community-based maintenance. The Nira AF85 pump is not in the public domain. For specifications and information, it is necessary to contact the manufacturer.
The Nira AF-85 Direct Action Handpump is based on a buoyant pump rod that is directly articulated by the user, discharging water at the up- & down stroke. The Nira AF-85 Pump is completely corrosion resistant.
The story of Nira Pumps Oy began in 1919 when the metal worker Niilo Ranni founded the Vammalan Konepaja . The company started manufacturing well pumps in the 1930s. Today, Nira hand pumps are used in over 50 countries, from the dusty heat of Africa to the freezing Arctic. Manufacturing began in the 1930s and hundreds of thousands of pumps are still in use in Finland. Since then:
- 1976 the first well pumps exported to Africa.
- 1985 Nira AF85 hand operated pump was a test winner in the World Bank's field and laboratory tests.
- 1992 Nira starts Tanira Ltd in Tanzania. Key components are shipped from Finland.
 Many design of locally produced suction pumps are available, most of them are family pumps. In contrast to the community pumps, these pumps are normally not standardised. Their design and functioning is largely dependent on the materials that are locally available and on the user preference.
Many design of locally produced suction pumps are available, most of them are family pumps. In contrast to the community pumps, these pumps are normally not standardised. Their design and functioning is largely dependent on the materials that are locally available and on the user preference.
The No. 6 Pump is a lever operated suction pump for shallow wells. Typically, No. 6 Pumps are installed in collapsible tube wells with the screen extending to the coarse sand aquifer.
It is designed for family use, serving up to 100 persons. The maximum possible lift is 7 m. The No. 6 pump is a public domain pump defined by RWSN specifications. It is easy to install and has excellent potential for community based maintenance.
In Madagascar, this type of pump is known as they 'Tany' pump and is one of the most common types found on the island.
Many hundreds of types of handpump are in use around the world, from home-made inventions to protected commercial designs. The most comprehensive overview of handpump types remains "Community Water Supply: The Handpump Option" Arlosoroff et all (1987), but some designs have emerged since.
Disclaimer: The following list is not exhaustive and does not represent an endorsement by RWSN or Skat.
We welcome the submission of further information and documentation on different designs.
 The Rope Pump features a unique design in which small plastic pistons are lined up on a rope. The distance between the pistons is approximately 1 m. The drive wheel is crank operated and pulls the rope through a plastic rising pipe. The drive wheel consists of cut old tires. A concrete guide box with a glass bottle at the well ground leads the rope with the pistons into the rising main pipe.
The Rope Pump features a unique design in which small plastic pistons are lined up on a rope. The distance between the pistons is approximately 1 m. The drive wheel is crank operated and pulls the rope through a plastic rising pipe. The drive wheel consists of cut old tires. A concrete guide box with a glass bottle at the well ground leads the rope with the pistons into the rising main pipe.
RWSN work has particularly focused on rope pumps in Nicaragua, Madagascar and Mozambique and public domain standards and guidlines have been produced.
 Google Übersetzer
Google Übersetzer

